A Comprehensive Benchmark on Spectral GNNs: The Impact on Efficiency, Memory, and Effectiveness
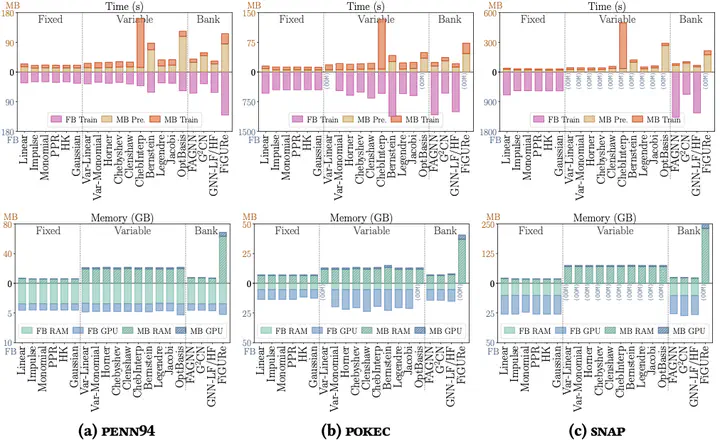
Time and memory efficiency comparison of spectral filters.
A comprehensive benchmark on spectral GNNs relating efficiency and effectiveness.
With recent advancements in graph neural networks (GNNs), spectral GNNs have received increasing popularity by virtue of their ability to retrieve graph signals in the spectral domain. These models feature uniqueness in efficient computation as well as rich expressiveness, which stems from advanced management and profound understanding of graph data. However, few systematic studies have been conducted to assess spectral GNNs, particularly in benchmarking their efficiency, memory consumption, and effectiveness in a unified and fair manner. There is also a pressing need to select spectral models suitable for learning specific graph data and deploying them to massive web-scale graphs, which is currently constrained by the varied model designs and training settings. In this work, we extensively benchmark spectral GNNs with a focus on the spectral perspective, demystifying them as spectral graph filters. We analyze and categorize 35 GNNs with 27 corresponding filters, spanning diverse formulations and utilizations of the graph data. Then, we implement the filters within a unified spectral-oriented framework with dedicated graph computations and efficient training schemes. In particular, our implementation enables the deployment of spectral GNNs over million-scale graphs and various tasks with comparable performance and less overhead. Thorough experiments are conducted on the graph filters with comprehensive metrics on effectiveness and efficiency, offering novel observations and practical guidelines that are only available from our evaluations across graph scales. Different from the prevailing belief, our benchmark reveals an intricate landscape regarding the effectiveness and efficiency of spectral graph filters, demonstrating the potential to achieve desirable performance through tailored spectral manipulation of graph data.
🏆 Awarded by the PREMIA Best Student Paper Awards 2025, Certificate of Commendation, Singapore (2 nationwide)